1. Introduction to Componente Server and Its Significance
In today’s digital landscape, servers form the backbone of virtually every modern IT infrastructure. Whether supporting enterprise applications, hosting websites, or managing extensive databases, the performance and reliability of a server depend heavily on its core componente server. These fundamental hardware parts collectively ensure that a server operates efficiently, securely, and continuously. Understanding the intricacies of server components is crucial for IT professionals, system integrators, and businesses aiming to optimize operational uptime and scalability.
Understanding the Role of Server Components
Each server component has a specific role that contributes to the overall functionality. The processor (CPU) acts as the brain, executing commands and managing data flow. Memory modules (RAM) provide the necessary workspace for rapid data access, while storage drives store all digital information, from operating systems to critical company data. Supporting components like motherboards, power supplies, and network cards ensure stability and connectivity, forming an interconnected ecosystem that facilitates seamless server operation.
Why Selecting the Right Componente Server Matters
Selecting appropriate server components is not a mere hardware decision; it directly impacts performance metrics such as processing speed, data throughput, and system uptime. Inappropriate choices can lead to bottlenecks, increased downtime, or inadequate scalability to support future growth. For instance, choosing a high-performance CPU without compatible memory or storage can underutilize the processor’s capabilities, leading to wasted investment. Thorough knowledge and strategic selection of components are essential for deploying reliable, future-proof infrastructure that aligns with organizational goals.
Key Benefits of a Well-Configured Server
- Enhanced Performance: Optimized components ensure faster processing, better multitasking, and quicker data access.
- Increased Reliability: High-quality parts reduce the risk of hardware failures, minimizing downtime.
- Scalability: Modular components allow for easy upgrades as demands grow.
- Cost Efficiency: Durable and compatible parts lower maintenance costs and extend hardware lifespan.
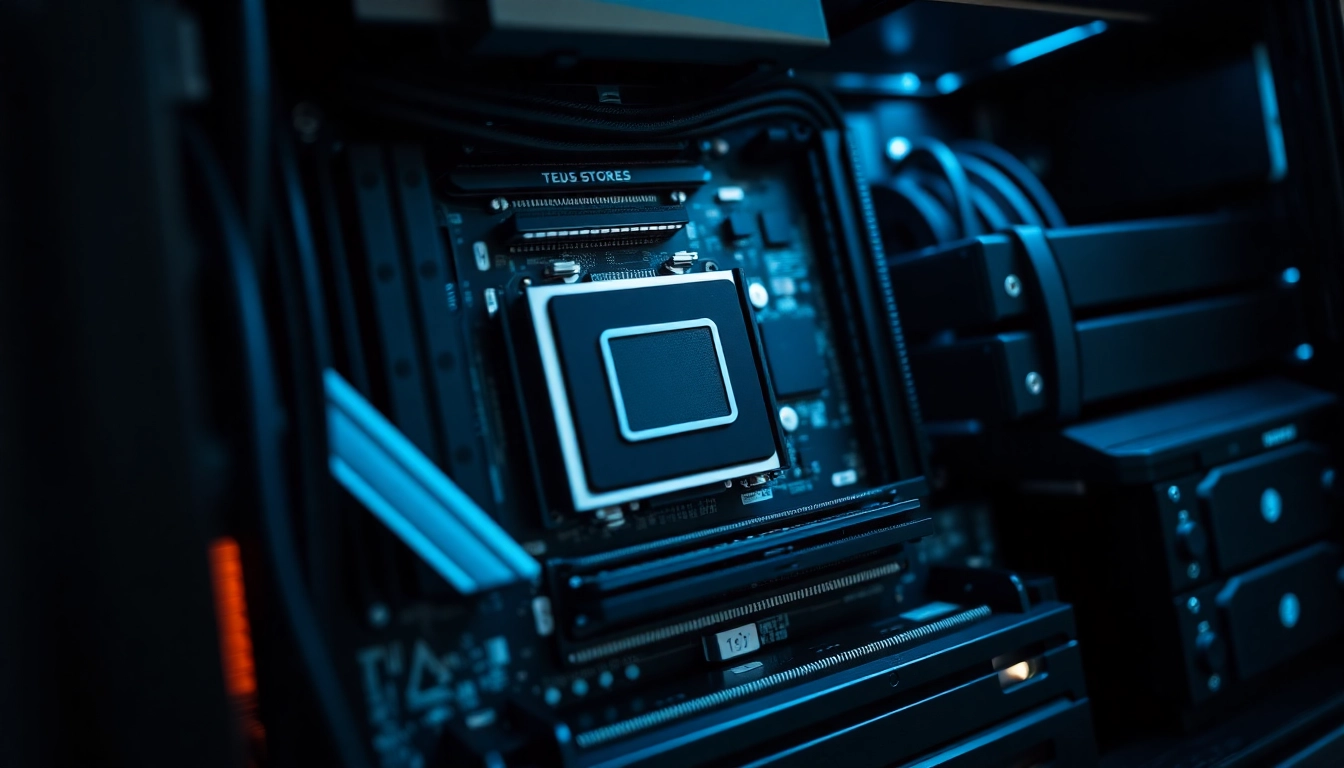
2. Core Hardware Elements of a Componente Server
Processor (CPU): The Brain of Your Server
The CPU is the central processing unit that handles all data computation and task execution. In mission-critical environments, selecting a processor with multiple cores and high clock speeds is vital. Enterprise-grade CPUs like Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC offer features such as multi-threading, larger cache sizes, and support for error-correcting code (ECC) memory—ensuring stability during intensive workloads. For example, servers with powerful processors can handle virtualization, large database operations, and complex computations efficiently.
Memory Modules (RAM): Ensuring Speed and Stability
RAM acts as the server’s short-term memory, facilitating rapid data access for active applications. The choice between DDR4 and DDR5 memory, along with the capacity (e.g., 32GB, 64GB, or more), influences performance. ECC RAM is highly recommended for servers because it detects and corrects data corruption, enhancing stability. Proper memory configuration, such as dual-channel arrays, can significantly optimize bandwidth and reduce latency, thereby improving overall throughput during high-demand tasks.
Storage Drives: Hard Disk vs SSD Explained
Storage drives are critical for data persistence and speed. Traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), such as the Seagate Constellation ES.3 3TB SAS disks, offer large capacities at a lower cost but with slower read/write speeds. Solid-State Drives (SSD), like Dell’s SATA SSD D3-S4520 480GB, provide rapid data access, reduced latency, and increased reliability—ideal for hosting operating systems and frequently accessed applications. NVMe SSDs, leveraging the PCIe interface, further accelerate workloads with transfer speeds exceeding 3GB/s, making them the optimal choice for high-performance servers.
3. Supporting Components for Reliable Server Operations
Motherboards and Chipsets
The motherboard serves as the main circuit hub, connecting all server components. Selecting a server-grade motherboard with robust chipsets ensures compatibility with high-core-count CPUs, large memory modules, and multiple expansion cards. Features like integrated RAID controllers, multiple PCIe slots, and extensive I/O ports facilitate high-throughput connections and data redundancy—key for maintaining uptime and performance. For example, motherboards supporting advanced chipset technologies enable efficient resource management across different hardware subsystems.
Power Supply Units (PSU): Powering Performance
Reliable power is essential for server stability. High-efficiency PSUs, ideally with 80 Plus Platinum certification, minimize energy waste and heat generation. Redundant power supplies further ensure continuous operation even if one unit fails. With capacities often exceeding 750W for high-performance servers, PSUs must be matched to the total power consumption of all components, including multiple GPUs or extensive storage arrays, such as in Dell PowerEdge servers equipped with dual CPUs and advanced RAID controllers.
Network Interface Cards and Connectivity
Fast, stable network connectivity is vital for data-intensive workloads. Standard gigabit Ethernet ports are often insufficient for enterprise needs. Upgrading to 10Gb or 25Gb SFP28 NICs, like the Intel XXV710-DA2 Dual Port 25Gb SFP28 cards, dramatically improves data transfer rates, reduces latency, and enhances overall network throughput. This is especially important for data centers, cloud environments, and high-frequency trading platforms, where every millisecond counts.
4. Configuring and Upgrading Your Componente Server
Choosing Compatible Components
Compatibility is paramount when selecting server hardware. Ensuring dimensions, interface types, and supported standards align prevents costly delays and hardware failures. Consulting manufacturer specifications, such as those for specific models like Dell R640 or HPE ProLiant ML110 Gen10, provides assurance of compatibility. Combining high-end CPUs with matching RAM and storage controllers maximizes performance without bottlenecks.
Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation involves meticulous handling, static discharge precautions, and adherence to vendor guidelines. Regular firmware updates for BIOS, RAID controllers, and network cards enhance security and stability. Routine hardware diagnostics and monitoring—using tools like Dell OpenManage or HPE Integrated Lights-Out (iLO)—enable early detection of potential failures, thus minimizing downtime.
Performance Optimization Tips
Optimizing server performance includes configuring BIOS settings for maximum efficiency, enabling hardware acceleration, and balancing workload distribution across CPUs and memory channels. Implementing RAID configurations tailored to your workload, like RAID 10 for Redundancy or RAID 5 for capacity, improves data integrity and speed. Caching frequently accessed data on SSDs and leveraging high-speed networking further accelerates system performance.
5. Future Trends and Innovations in Server Components
Emerging Technologies in Componente Server
The landscape of server hardware is rapidly evolving. Innovations such as AI-optimized CPUs, persistent memory, and high-bandwidth interconnects dominate the horizon. The integration of FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays) and specialized accelerators enhances computational capabilities for machine learning and scientific computing.
The Impact of NVMe and High-Speed Networks
NVMe technology revolutionizes storage by reducing latency and increasing throughput, especially when combined with PCIe 4.0 or 5.0 interfaces. Simultaneously, advancements in network infrastructure—like 25Gb, 50Gb, and even 100Gb Ethernet—are enabling data centers to handle colossal data volumes with minimal delay, supporting critical applications such as real-time analytics and cloud-native platforms.
How to Keep Your Infrastructure Future-Proof
To ensure longevity, organizations should adopt scalable architectures with modular components. Emphasizing standardization and compatibility, investing in high-quality hardware, and staying updated with industry trends allow infrastructure to adapt seamlessly to emerging demands. Regular upgrades, along with comprehensive testing and proactive maintenance, are key strategies for maintaining a resilient and competitive server environment.